151-xxx Programming Mechanical Engineer
โดย ผศ.สราวุฎฐ์ วรสุมันต์ , ประยุทธ พันธุลาภ
Heat Transfer
Thermal conductivity of some selected gases, insulation products, aluminum, asphalt, brass, copper, steel and other common materials
Viscosity of Water
Viscosity of Water
Advance Topics
Numerical solutions with GNU OCTAVE
Octave and C compiler on-line
Click here to run ->
rextester.com
Loop Flow Chart
ข้อสอบ กว
%Example 1
t = 0:0.1:6.3;
plot (t, cos(t), "-;cos(t);", t, sin(t*0.5), "-b;sin(t);");
print -dpng some_name.png;
%Example 2
x=1:0.1:10;
plot(x, sin(x));
print -dpng some_name.png;
%Example 3
A = [3,12; 4,2;]
C = [15; 6;]
x = inv(A)*C
%Example 4 Hydro static
rho = 1000 %kg/cu.m.
g = 9.81 %m/s2
h = 20 %m
p = rho * g * h %N/sq.m
ข้อสอบ กว
Example 05
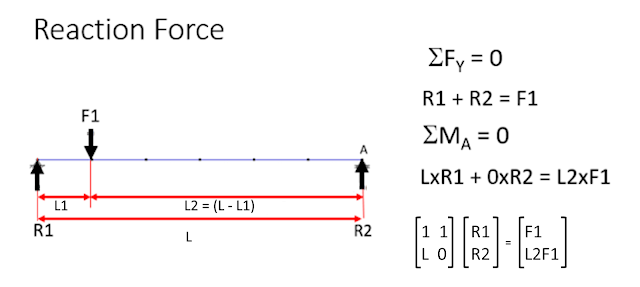
%*****Reaction at simple beam
printf("Student No.2\n")
printf("**************\n")
F1 = 150 %KN
L = 6 %m
L1 = 1 %m
L2 = L - L1
A = [1,1; L, 0;]
F = [F1; (L2*F1);]
R = inv(A)*F
printf("R1 = %6.3f\n",R(1))
printf("R2 = %6.3f\n",R(2))
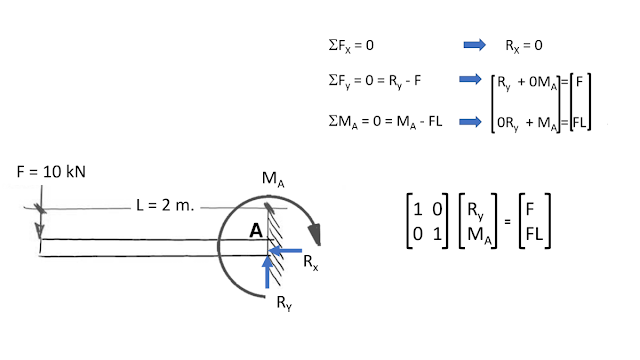 Example 06
Example 06
%****Cantiliver Beam
printf("Student No.1\n")
printf("**************\n")
F1 = 300 %KN
L = 2 %m
A = [1,0; 0, 1;]
F = [F1; (L*F1);]
R = inv(A)*F
printf("RY = %6.3f KN\n",R(1))
printf("MA = %6.3f KN.m\n",R(2))
Example 07
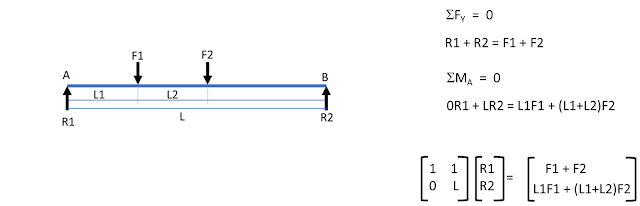
-->
%*****Reaction at simple beam F1 F2
printf("Student No.2\n")
printf("**************\n")
F1 = 100 %KN
F2 = 50 %KN
L = 6 %m
L1 = 1 %m
L2 = 1.2 %m
FT = F1 + F2 %total force
MT = (L1*F1) + ((L1+L2)*F2) %total moment
A = [1,1; 0, L;]
F = [FT; MT;]
R = inv(A)*F
printf("R1 = %6.3f\n",R(1))
printf("R2 = %6.3f\n",R(2))
Example 08
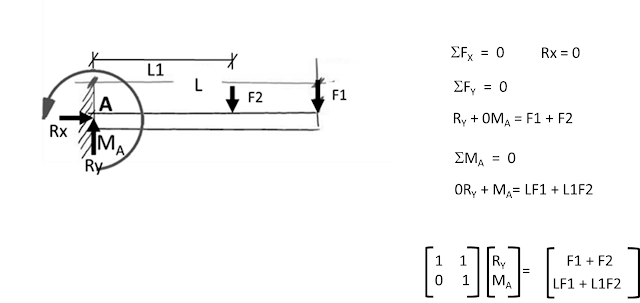
%*****Reaction at Cantilever Beam F1 F2
printf("Student No.2\n")
printf("**************\n")
F1 = 100 %KN
F2 = 50 %KN
L = 6 %m
L1 = 1 %m
FT = F1 + F2 %total force
MT = (L*F1) + (L1*F2) %total moment
A = [1,0; 0,1;]
F = [FT; MT;]
R = inv(A)*F
printf("RY = %6.3f\n",R(1))
printf("MA = %6.3f\n",R(2))
Example 09
%****Ex 9. Solve Matrix
printf("Student No.2\n")
printf("**************\n")
printf("**Solve Matrix***\n")
printf("**************\n")
A = [
-4, -11, 5, -5;
-11, -8, 10, -9;
-5, -5, 8, -7;
-2, -3, 8, -4;
]
F = [
-165;
-258;
-149;
-69;
]
disp "***********************"
R = inv(A)*F
printf("a = %6.3f \n",R(1))
printf("b = %6.3f \n",R(2))
printf("c = %6.3f \n",R(3))
printf("d = %6.3f \n",R(4))
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
// reads and stores input
scanf("%d", &number);
// displays output
printf("You entered: %d", number);
return 0;
}
พื้นฐานการเขียนโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์
(Programming Fundamentals)
Programming Fundamentals
การเขียนโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ C
Link->ข้อสอบ Computer Programming
https://www.onlinegdb.com/online_c_compiler
*****Open C Online*****
***C Examples***
Android Text Editor for Copy/Paste codes
Link-> Play Store Editor
C Keywords
***Link->C Keywords***
ความแตกต่างระหว่าง Error กับ Warning
การใช้ Comment
// นำหน้า หมายถึง compiler จะไม่สนใจตั้งแต่ // จนสิ้นสุดบรรทัดนั้น
/* */ คลุม หมายถึง compiler จะไม่สนใจตั้งแต่ /* จนถึง */
Link->C-input-output
Link->C-String
/* Example 1 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf ("Hello world!");
return 0;
}
/* Example 2 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
// reads and stores input
scanf("%d", &number);
// displays output
printf("You entered: %d", number);
return 0;
}
295
296
เอกสารประกอบการสอน if else, while, do while
*****Link->PDF*****
Relational Operator
Home Work#2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int i, found = 0;
char size[6]; //inch
char sv[20];
float dia = 0; //m.
float r = 0; //m.
float flow = 0; //cu.m./s
float v = 2; // m/s
char pipe_size[5][20] = {
"1","2","3","4","6"
}, name[10];
char pipe_diam[5][20] = {
"28.0","51.4", "76.2", "97.8", "141.6"
}, data[10];
printf("Enter Size [inch]: ");
scanf("%s",size);
printf("Enter Velocity [m/s]: ");
scanf("%s",sv);
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
if(strcmp(size, pipe_size[i]) == 0 )
{
found = 1;
//printf("data = %s" ,pipe_diam[i] );
sscanf(pipe_diam[i] , "%f", &dia); //convert string to float
sscanf(sv , "%f", &v); //convert string to float
r = (dia * 0.5) / 1000.0; //mm
flow = v * (3.14159 * r * r) * 1000; //liter/s
printf("flow [liter/s] = %f" , flow);
break; //out of for loop
}
}
return 0;
}
Home Work#1
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int cpucore = 8;
int camera = 3;
int ram = 64;
if (camera<2)
{
printf("Camera NOT Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("Camera Pass\n");
}
if (cpucore>4)
{
printf("CPU CORE Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("CPU CORE NOT pass\n");
}
if (ram>32)
{
printf("RAM Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("RAM NOT pass\n");
}
return 0;
}
การใช้ if else
//***Example if 1***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 20;
int y = 22;
if (x<y)
{
printf("Variable x is less than y");
}
return 0;
}
//***Example if else***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 20;
int y = 22;
if (x<y)
{
printf("Variable x is less than y");
}
else
{
printf("Variable x is NOT less than y");
}
return 0;
}
การใช้ for loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 18;
int height = 155;
int weight = 42;
if (height<=150)
{
printf("height NOT Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("height Pass\n");
}
if (age<=20)
{
printf("age Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("age NOT pass\n");
}
if (weight<=80)
{
printf("weight Pass\n");
}
else
{
printf("weight NOT pass\n");
}
return 0;
}
//***Example Loop 1***
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int a;
int b;
b = 1;
/* for loop execution */
for( a = 5; a > 0; a = a - 1 ){
b = b + 2;
printf("value of a: %d b: %d\n ", a ,b);
//printf("value of b: %d\n", b);
}
return 0;
}
//***Example for loop sum***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int sum;
sum = 0;
for (i=1; i<=3; i++)
{
sum = sum + i;
printf("%d\n", sum);
}
return 0;
}
//***Example for loop average***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
float sum;
float avg;
sum = 0;
for (i=1; i<=6; i++)
{
sum = sum + i;
printf("i=%d , sum=%f\n", i,sum);
}
printf("i=%d \n",i);
//reduce i by 1
i = i - 1;
printf("***i=%d*** \n",i);
avg = sum / (float)i;
printf("%6.3f\n", avg);
return 0;
}
//***Example for loop array***
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int n[4][4]; /* n is an array of 3X3 integers */
int i,j;
for ( i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) {
for ( j = 0; j < 4; j++ ) {
n[j][i] = i; /* set element at location n[j][i] = i */
printf("n[%d][%d] = %d\n", i,j,n[j][i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
การใช้ while loop
//***Example While Loop 1***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int count=1;
while (count <= 4)
{
printf("%d ", count);
count++;
}
return 0;
}
//***Example While Loop 2***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x;
int y;
x = 5;
y = 2;
while (x > 0)
{
x = x - 1;
y = y * x;
printf("y = %d \n ", y);
}
return 0;
}
//***Example While Loop 3***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
int j;
i = 1;
j = 0;
for ( i = 1; i <= 4; i++ ) {
if ((i-1)/2 == 0)
{
printf("i = %d \n ", i);
j = i +1;
}
}
return 0;
}
การใช้ do while loop
//***Example Do While Loop 1***
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int j=0;
do
{
printf("Value of variable j is: %d\n", j);
j++;
}while (j<=3);
return 0;
}
/* Example 3.1 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
short a;
long b;
long long c;
long double d;
printf("size of short = %d bytes\n", sizeof(a));
printf("size of long = %d bytes\n", sizeof(b));
printf("size of long long = %d bytes\n", sizeof(c));
printf("size of long double= %d bytes\n", sizeof(d));
return 0;
}
/* Example 3.2 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
short a;
long b;
long long c;
long double d;
printf("size of short = %d bytes\n", (int)sizeof(a));
printf("size of long = %d bytes\n", (int)sizeof(b));
printf("size of long long = %d bytes\n", (int)sizeof(c));
printf("size of long double= %d bytes\n", (int)sizeof(d));
return 0;
}
/* Example 4 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char chr = 'a';
printf("character = %c.", chr);
return 0;
}
/* Example 5 */
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char first[100], last[100];
int i;
printf("nEnter your first name:");
scanf("%s", first );
printf("nEnter your last name:");
scanf("%s", last );
printf("nYour full name is: %s %sn", first, last );
printf("First name is: ");
for( i=0; i<100; i++ ){
if ((first[i] > 32) && (first[i] < 123)){
printf("%c ",first[i]);
}
}
printf("nLast name is: ");
for( i=0; i<100; i++ ){
printf("%c ",last[i]);
}
printf("n");
return 0;
}
การเขียนโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ Octave
https://octave-online.net/
*****Open Octave Online*****
- Run Octave

- หน้าจอของโปรแกรม Octave

- Command Window
- Editor

Octave แก้ระบบสมการ
ระบบสมการ
->Link1
A = [1,1,1; 0,2,5; 2,5,-1;]
C = [6;-4;27;]
x = inv(A) * C
x
Introduction to Octave
#
i = 2 * 4
i
#
x = 0 : 0.1 : 1;
x
y = [ 0 : 0.1 : 1];
y
#แก้ระบบสมการ
A = [1,1,1; 0,2,5; 2,5,-1;]
C = [6;-4;27;]
x = inv(A) * C
x
######plot1###############
x = 1:5; y = 1:5;
plot (x,y,"g");
title ("plot() of green line at 45 degrees");
######plot2###############
x = 1:5; y = 1:5;
plot (x,y,"g*");
title ("plot() of green stars along a line at 45 degrees");
###### plot function 1 #########
x = -10:0.1:10;
plot (x, sin (x));
###### plot function 2 #########
x = -10:0.1:10;
y = sin(x);
plot (x, y);
###### plot function 3 #########
x1 = 1:5; y1 = 1:5;
x2 = 5:9; y2 = 5:-1:1;
plot (x1,y1,"bo-", x2,y2,"rs-");
axis ("tight");
title ({"plot() of blue circles ascending and red squares descending";
"connecting lines drawn"});
###### plot function 4 #########
x = [0:10]';
y = [sin(x), cos(x)]
h = stem (x, y);
set (h(2), "color", "g");
set (h(1), "basevalue", -1)
###### Histogram 1 #########
hist (randn (10000, 1), 30);
###### Histogram 2 #########
h = bar (rand (5, 10));
set (h(1), "basevalue", 0.5);
###### Histogram 3 #########
h = bar (rand (10, 3));
set (h(1), "facecolor", "r")
set (h(2), "facecolor", "g")
set (h(3), "facecolor", "b")
###### Rose Map #########
[th, r] = rose ([2*randn(1e5,1), pi + 2*randn(1e5,1)]);
polar (th, r);
###### Contour 1 #########
x = 0:2;
y = x;
z = x' * y;
contour (x, y, z, 2:3)
###### Contour 2 #########
[x, y, z] = peaks (50);
contourf (x, y, z, -7:9)
***********************************
Sheet
*******************************************
<.p>
แก้ระบบสมการ
->Link1
A = [1,1,1; 0,2,5; 2,5,-1;]
C = [6;-4;27;]
x = inv(A) * C
x
Assignment 1/2019
***เลยกำหนดส่ง 5 ม.ค. 2563***